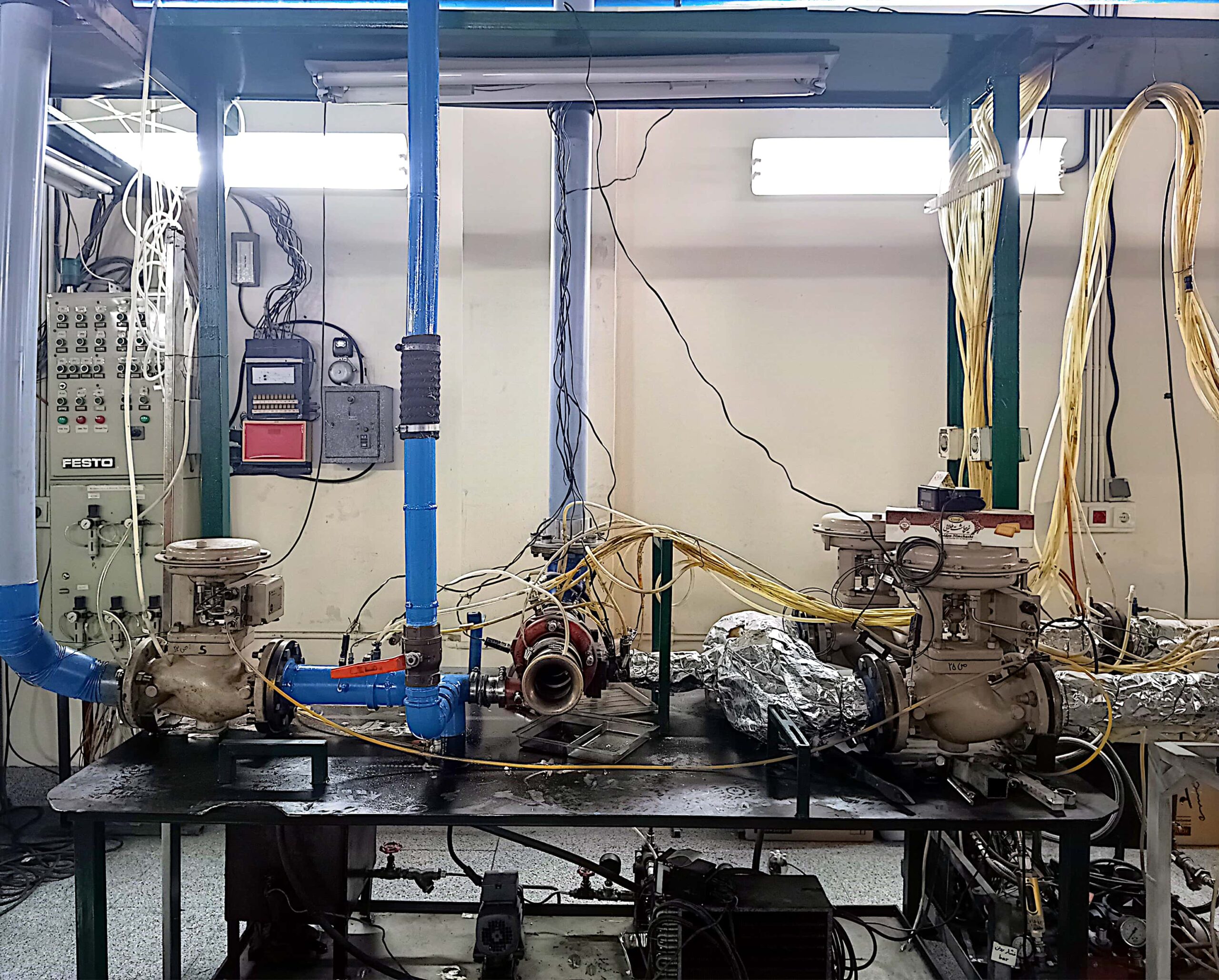
Turbocharger Test Lab
Sample Turbocharger Test Lab Circuits
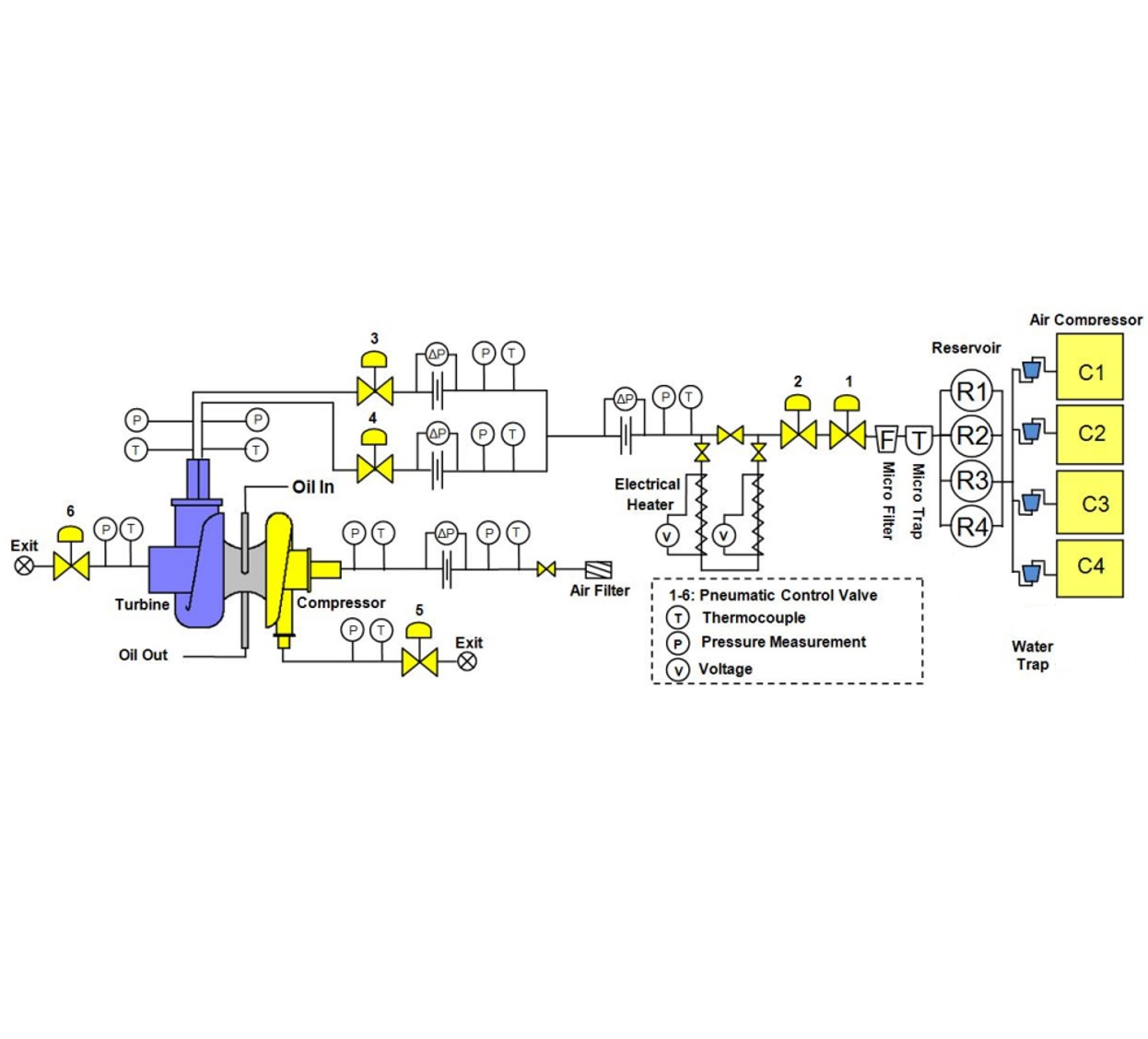
Turbocharger cold test circuit diagram
Turbocharger hot test circuit diagram
Turbocharging test circuit diagram
Table of contents
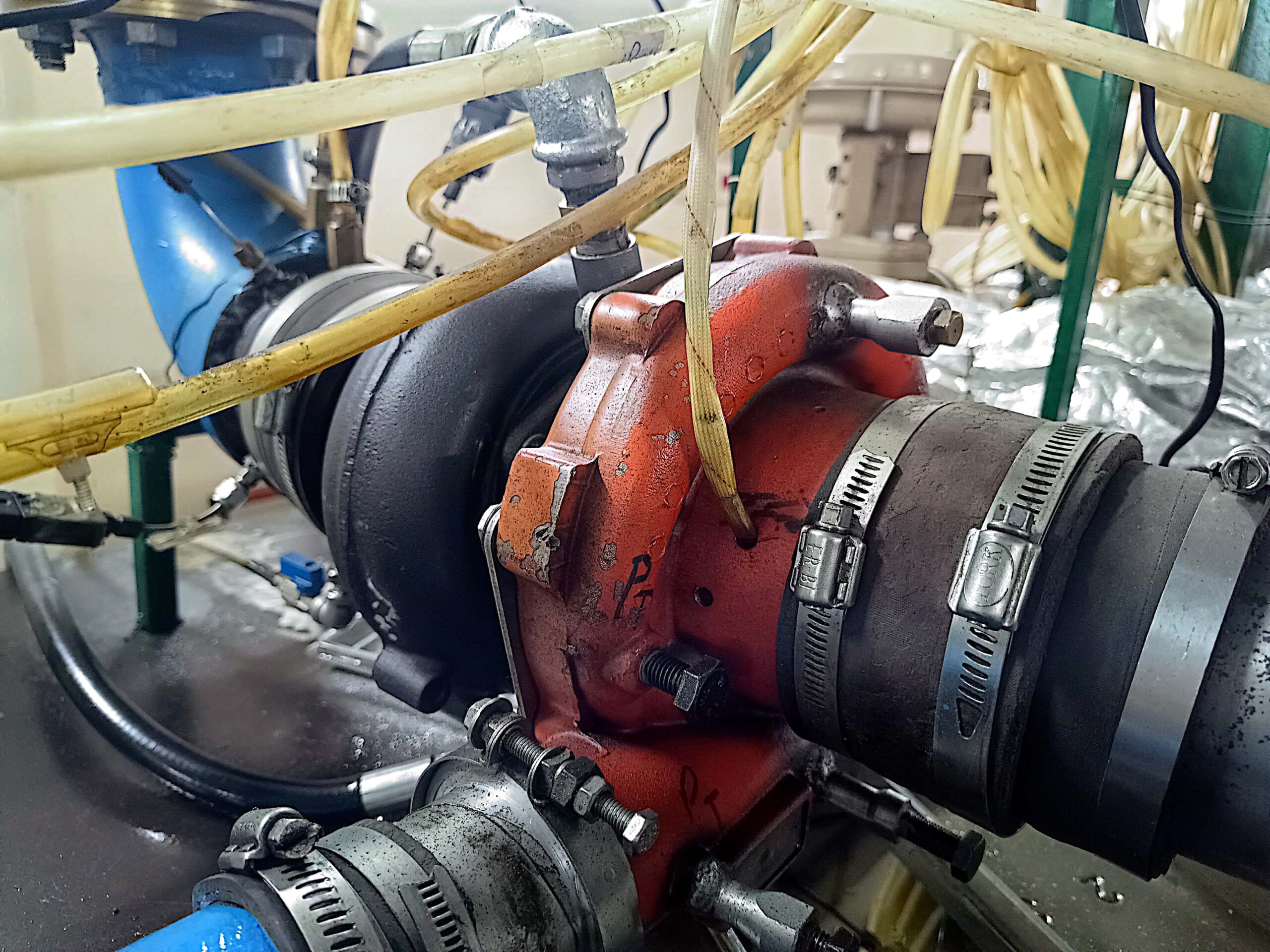
Hot Turbocharger Test Rig
Introduction
A hot turbocharger test rig is a mechanical system that uses the energy from engine exhaust gases to drive a turbine, which in turn forces more compressed air into the engine. This process increases engine power and efficiency. To simulate real-world operating conditions, the hot turbocharger test rig must be capable of reproducing the following:
High temperature: Simulation of temperatures exceeding 800–1000°C for optimal performance.
High pressure: Testing at high pressures to ensure component durability.
Dynamic conditions: Rapid changes in engine speed and gas flow.
Key Features of Hot Turbocharger Test Rig
Control and Data Acquisition System
Temperature sensors: Various thermocouples for temperature measurement.
Pressure sensors: Pressure sensors with suitable ranges for measuring inlet and outlet gas pressure.
Flow meters: Precise measurement of air and gas flow.
Compressed Air Supply
Screw compressor for supplying compressed air.
Compressed air storage tanks.
Lubrication System
Use of temperature-resistant oils.
Combustion Chamber
This section is used to heat the compressed air entering the turbine.
Turbocharger Under Test
This is the heart of the test rig, where performance data is collected.
Capabilities of Hot Turbocharger Test Rig
Theoretical and experimental studies on components of various turbochargers regarding behavioral characteristics and flow field.
Complete testing and data acquisition of turbine and compressor using manual and computer-based data acquisition systems in cold and hot tests.
Extraction of turbine and compressor behavioral characteristics from experimental results under various operating conditions, along with error analysis.
Various modeling of turbine and compressor for behavior prediction and model evaluation against experimental results.
Design and optimization of turbocharger turbine and compressor.
Sample Completed Projects
Theoretical and experimental investigation of losses in a radial-flow twin-entry gas turbine under full and partial admission conditions.
Design and performance optimization of a centrifugal compressor casing and evaluation with experimental results.
Design, optimization, and numerical/experimental evaluation of a centrifugal compressor impeller under geometric constraints.
Identification of surge phenomenon in centrifugal compressors, investigation of influencing factors, and prevention methods.
Applications of Hot Turbocharger Test Rig
Automotive industry: Performance testing of turbochargers in passenger and commercial vehicles.
Marine industry: Evaluation of turbochargers used in ship engines.
Aerospace industry: Testing of turbochargers for aircraft engines.
Academic research: Simulation and study of turbocharger performance under various conditions.
Advantages of Professional Design
Increased accuracy in test results.
Cost reduction through optimal materials and design.
Test repeatability for turbocharger performance validation.
References for Hot Turbocharger Test Rig
Cold Turbocharger Test Rig
Introduction
A cold turbocharger is a device that compresses the intake air to the engine, improving engine efficiency. The term “cold” is used because no combustion occurs in this process.
High pressure: Testing at high pressures to ensure component durability.
Dynamic conditions: Rapid changes in engine speed and gas flow.
Key Features of Cold Turbocharger Test Rig
Control and Data Acquisition System
Temperature sensors: Various thermocouples for temperature measurement.
Pressure sensors: Pressure sensors with suitable ranges for measuring inlet and outlet gas pressure.
Flow meters: Precise measurement of air and gas flow.
Compressed Air Supply
Screw compressor for supplying compressed air.
Compressed air storage tanks.
Lubrication System
Use of temperature-resistant oils.
Combustion Chamber
This section is used to heat the compressed air entering the turbine.
Turbocharger Under Test
This is the heart of the test rig, where performance data is collected.
Design Criteria for Cold Turbocharger Test Rig
Precise pressure control: Use of high-accuracy control valves.
Measurement accuracy: Advanced sensors with error less than 1%.
Circuit flexibility: Ability to quickly change settings for testing different conditions.
Types of Tests That Can Be Performed
Overall Performance Test: Evaluating turbocharger efficiency under real conditions.
Temperature and Pressure Test: Monitoring pressure and temperature changes at inlet and outlet.
Air Leakage Test: Identifying leakage points in the system.
Capabilities
Theoretical and experimental studies on components of various turbochargers regarding behavioral characteristics and flow field.
Complete testing and data acquisition of turbine and compressor using manual and computer-based data acquisition systems in cold and hot tests.
Extraction of turbine and compressor behavioral characteristics from experimental results under various operating conditions, along with error analysis.
Various modeling of turbine and compressor for behavior prediction and model evaluation against experimental results.
Design and optimization of turbocharger turbine and compressor.
Sample Completed Projects
Theoretical and experimental investigation of losses in a radial-flow twin-entry gas turbine under full and partial admission conditions.
Design and performance optimization of a centrifugal compressor casing and evaluation with experimental results.
Design, optimization, and numerical/experimental evaluation of a centrifugal compressor impeller under geometric constraints.
Identification of surge phenomenon in centrifugal compressors, investigation of influencing factors, and prevention methods.
Applications of Cold Turbocharger Test Rig
Automotive industry: Performance testing of turbochargers in passenger and commercial vehicles.
Marine industry: Evaluation of turbochargers used in ship engines.
Aerospace industry: Testing of turbochargers for aircraft engines.
Academic research: Simulation and study of turbocharger performance under various conditions.
Advantages of Professional Design
Increased accuracy in test results.
Cost reduction through optimal materials and design.
Test repeatability for turbocharger performance validation.
References for turbocharger performance validation.
Turbocharging Test Bench
Introduction
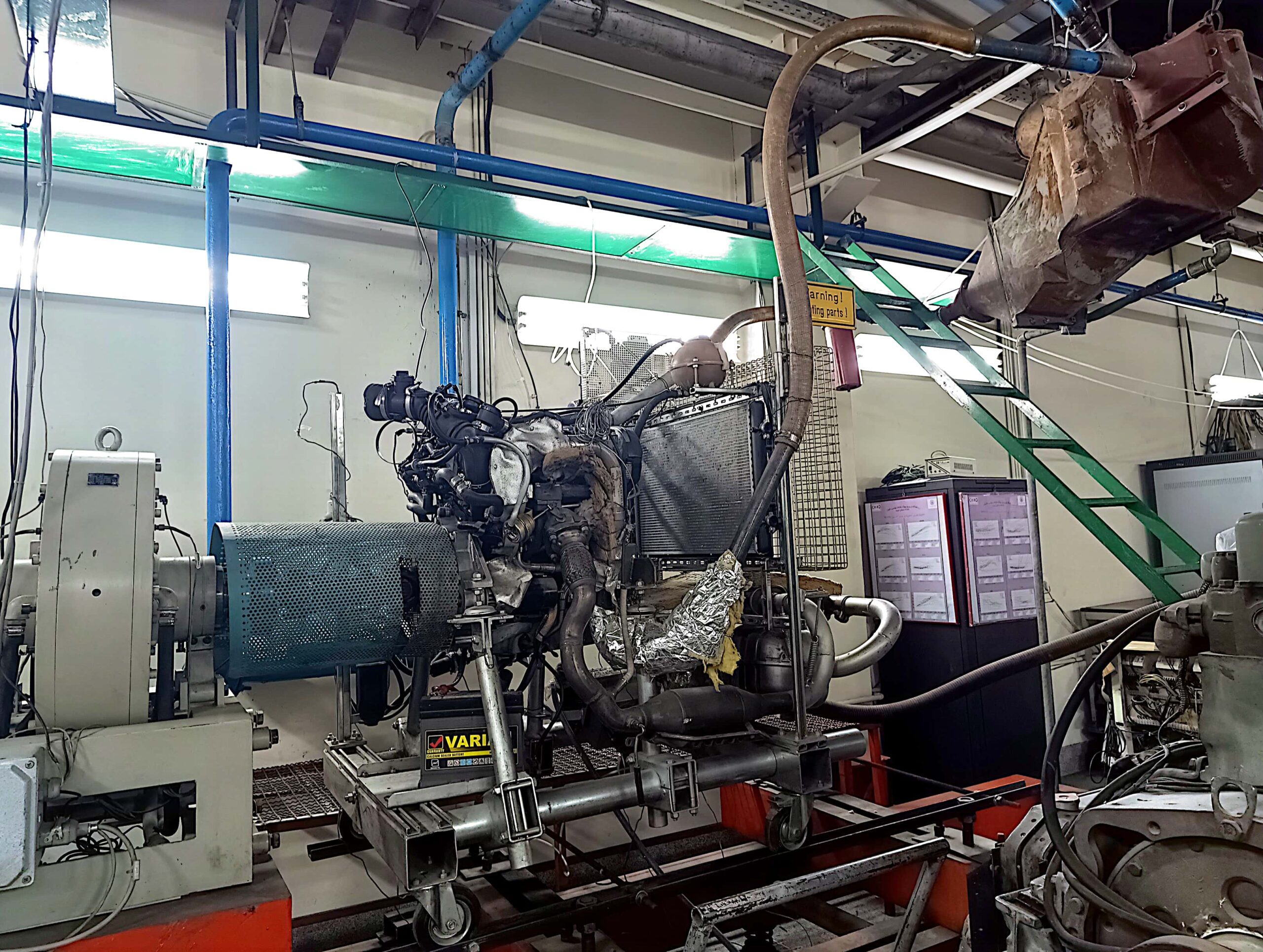
A turbocharger is an advanced technology used in automotive and industrial engines to increase output power and thermal efficiency. The turbocharger test bench is designed to simulate real-world operating conditions and provide precise performance data under various scenarios. Turbocharging refers to the process of using exhaust gases to drive a turbine that powers a compressor, forcing additional air into the engine for improved combustion.
Objectives of the Turbocharger Test Bench
Performance Evaluation
Assessment of rotational speed, inlet/outlet temperatures, and pressure ratio.
Thermal and Mechanical Efficiency Analysis
Measurement of how effectively exhaust gas energy is converted into mechanical work.
Design Optimization
Improvement of turbine and compressor blade geometry.
Durability and Reliability Testing
Identification of long-term weaknesses under continuous operation.
Main Components of the Turbocharger Test Bench
Turbine
Exhaust gases enter the turbine, extracting energy to drive the compressor.
Compressor
Compresses intake air before it enters the engine cylinders.
Internal Combustion Engine
The core of the test rig; data is collected from 4-cylinder gasoline or 6-cylinder natural-gas engines.
Lubrication System
Reduces friction and cools rotating components.
Cooling System
Cools hot exhaust gases and turbocharger oil.
Precision Sensors
Temperature, pressure, flow, and speed sensors for real-time data acquisition.
Control and Data Logging Unit
Collects, stores, and analyzes data from all sensors.
Key Parameters Measured
Pressure Ratio (Boost Pressure): Ratio of compressor outlet pressure to inlet pressure.
Various Efficiencies: Isentropic, mechanical, and total-to-total efficiencies.
Turbocharger Rotational Speed: Typically 50,000–250,000 RPM.
Mass Flow Rate: Air and exhaust gas flow rates.
Temperature Ratio Temperature changes: across compressor and turbine.
Benefits of Using the Test Bench
Increased Engine Efficiency
Optimized matching for higher power output.
Reduced Fuel Consumption
Better air–fuel mixing and combustion efficiency.
Lower Emissions
Reduced CO, HC, and NOx through optimized boost control.
Testing Under Extreme Conditions
Simulation of high-load, high-temperature, and transient operation.
Capabilities
Investigation of naturally aspirated engines and theoretical/experimental matching studies for turbocharging.
Theoretical and experimental studies on naturally aspirated diesel, gasoline, and CNG engines via performance testing and modeling.
Feasibility studies and implementation of turbocharging on naturally aspirated engines with necessary adjustments.
Determination of engine behavior (performance and emissions) in naturally aspirated and turbocharged states.
Performance enhancement of turbocharged engines through theoretical and experimental optimization.
Sample Completed Projects
Theoretical and experimental study of supercharging and turbocharging on gasoline engines.
Theoretical and experimental methods to reduce NOx emissions in turbocharged natural-gas engines.
Increasing power and reducing knock in turbocharged gasoline engines via charge-air cooling control.
Important Considerations in Design and Operation
Use of Heat- and Pressure-Resistant Materials Turbine and compressor components must withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive exhaust gases.
Precise Test Condition Control Accurate regulation of air/fuel flow, temperature, and load for repeatable results.
Real-Time Data Monitoring High-frequency sensors are essential for capturing transient behavior.
References of Turbocharging Test Rig
Table of contents
Turbocharger Test Lab
Cold Turbocharger Test Rig


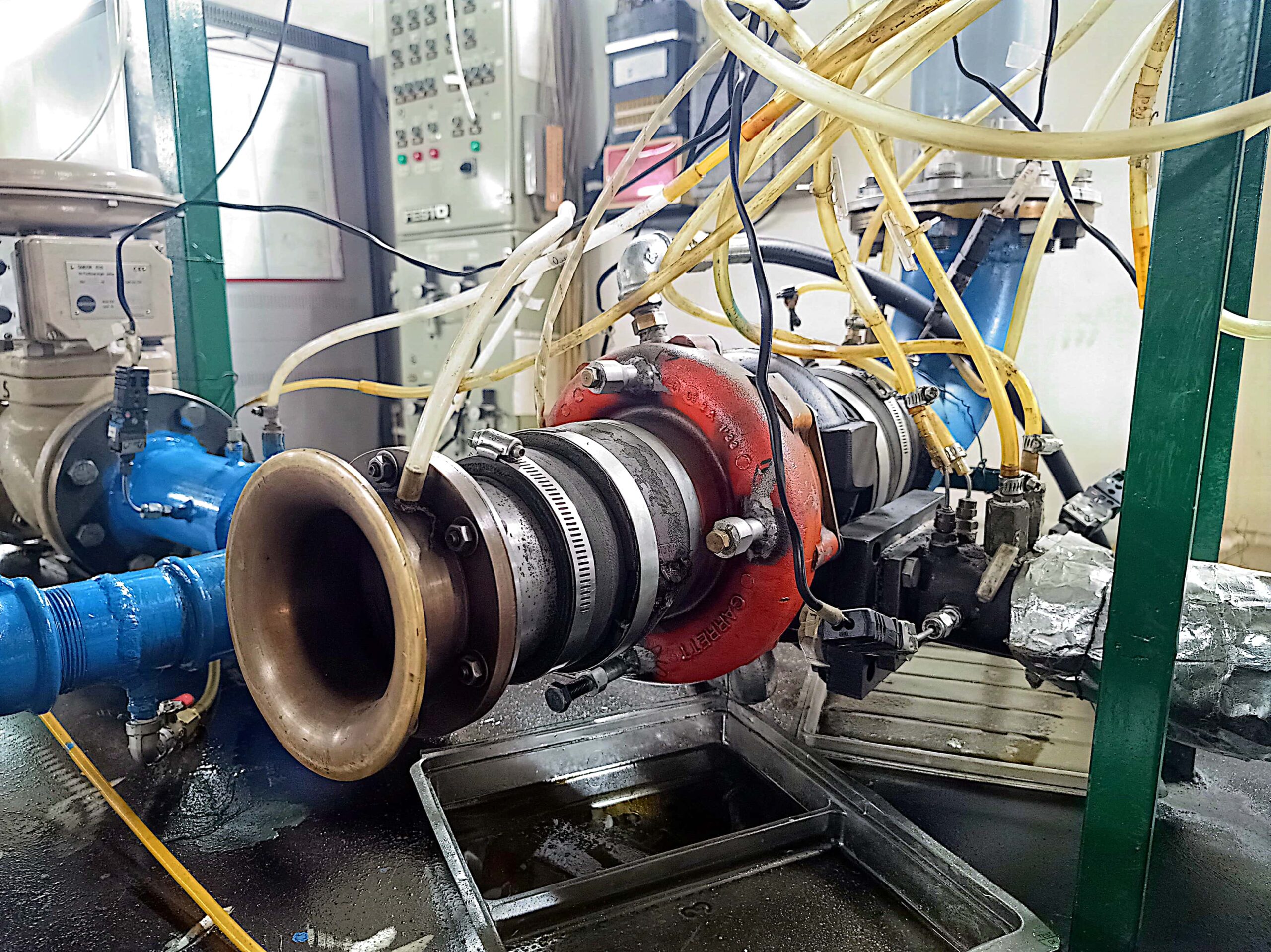


Hot Turbocharger Test Rig
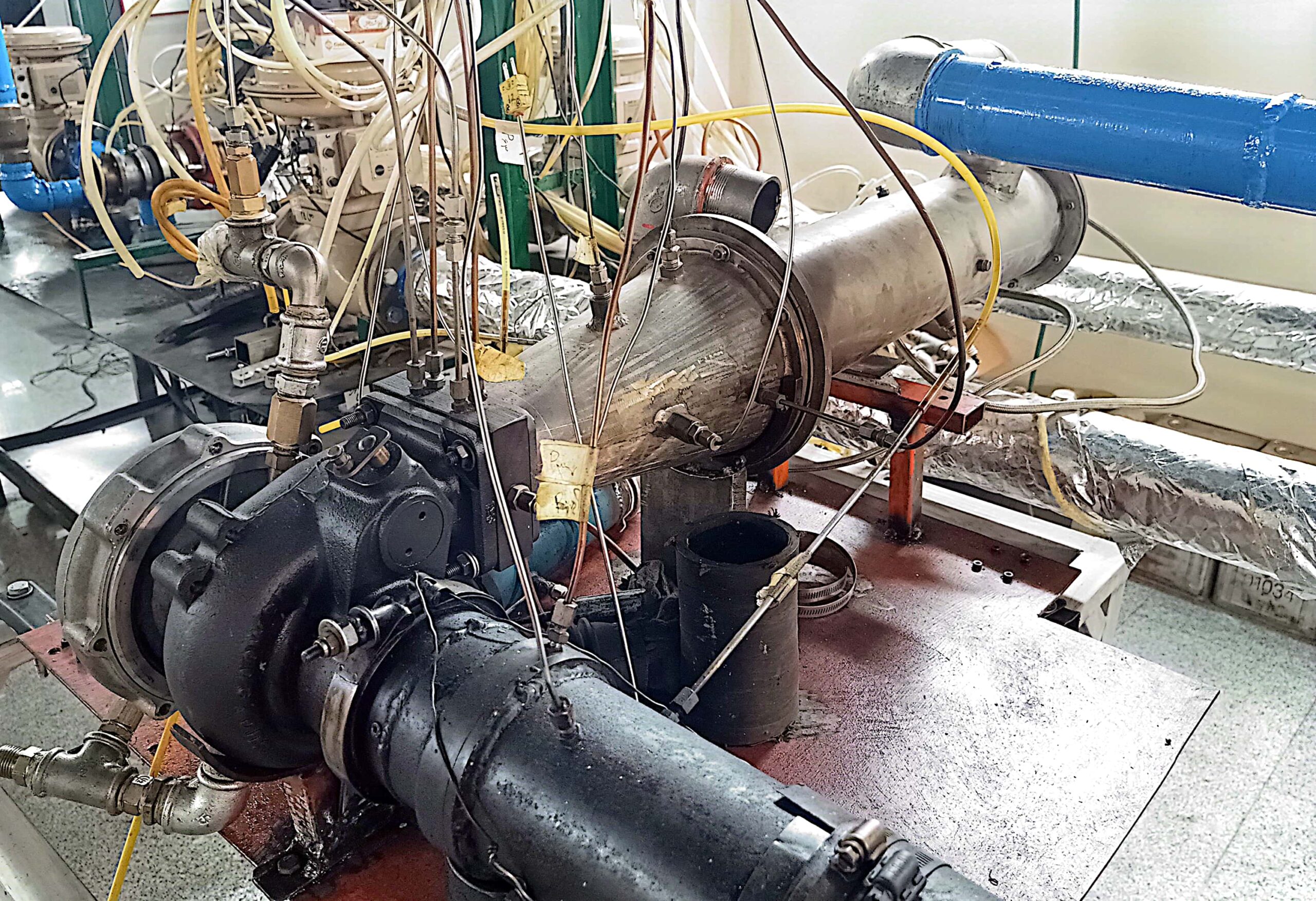
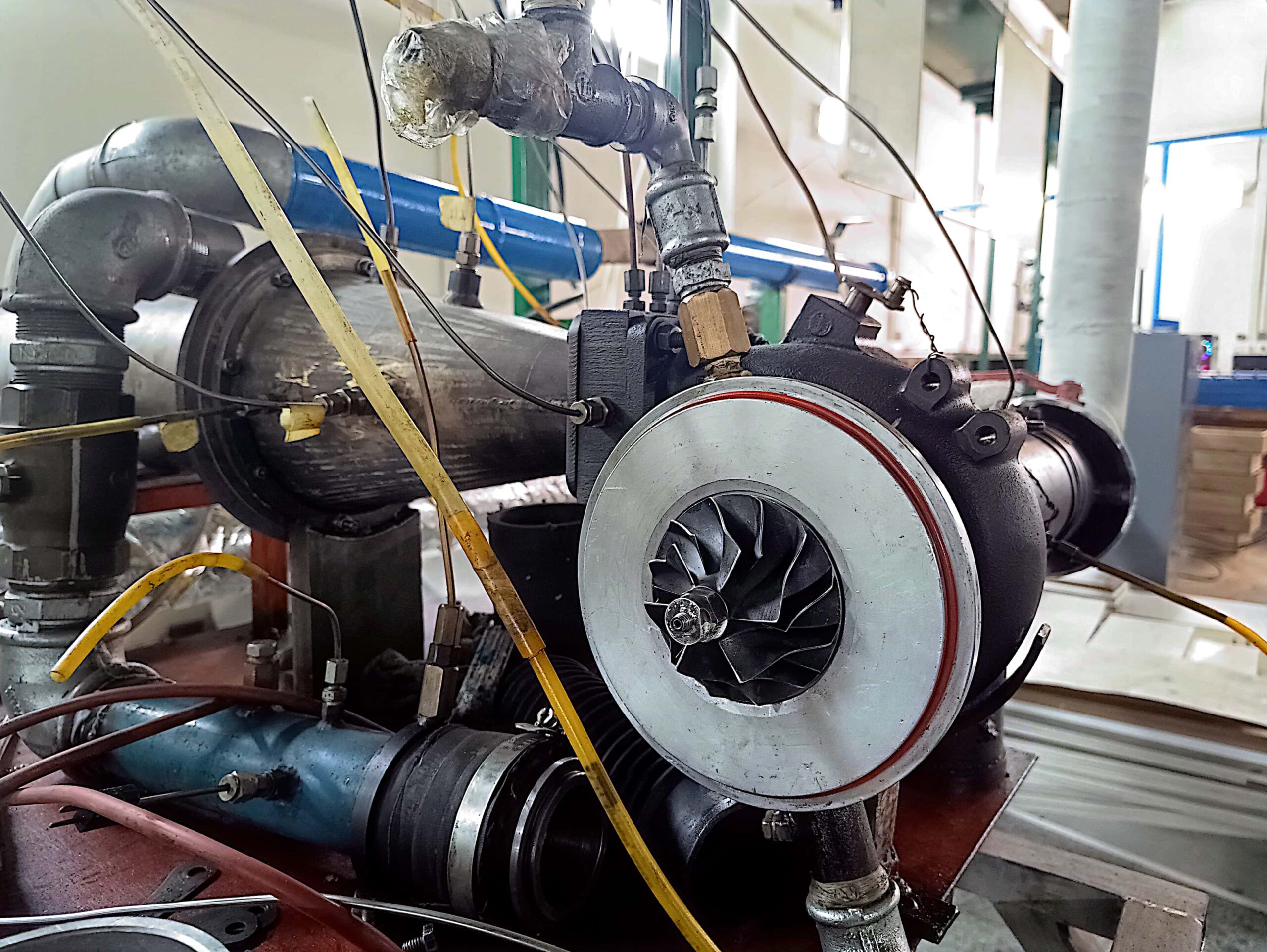


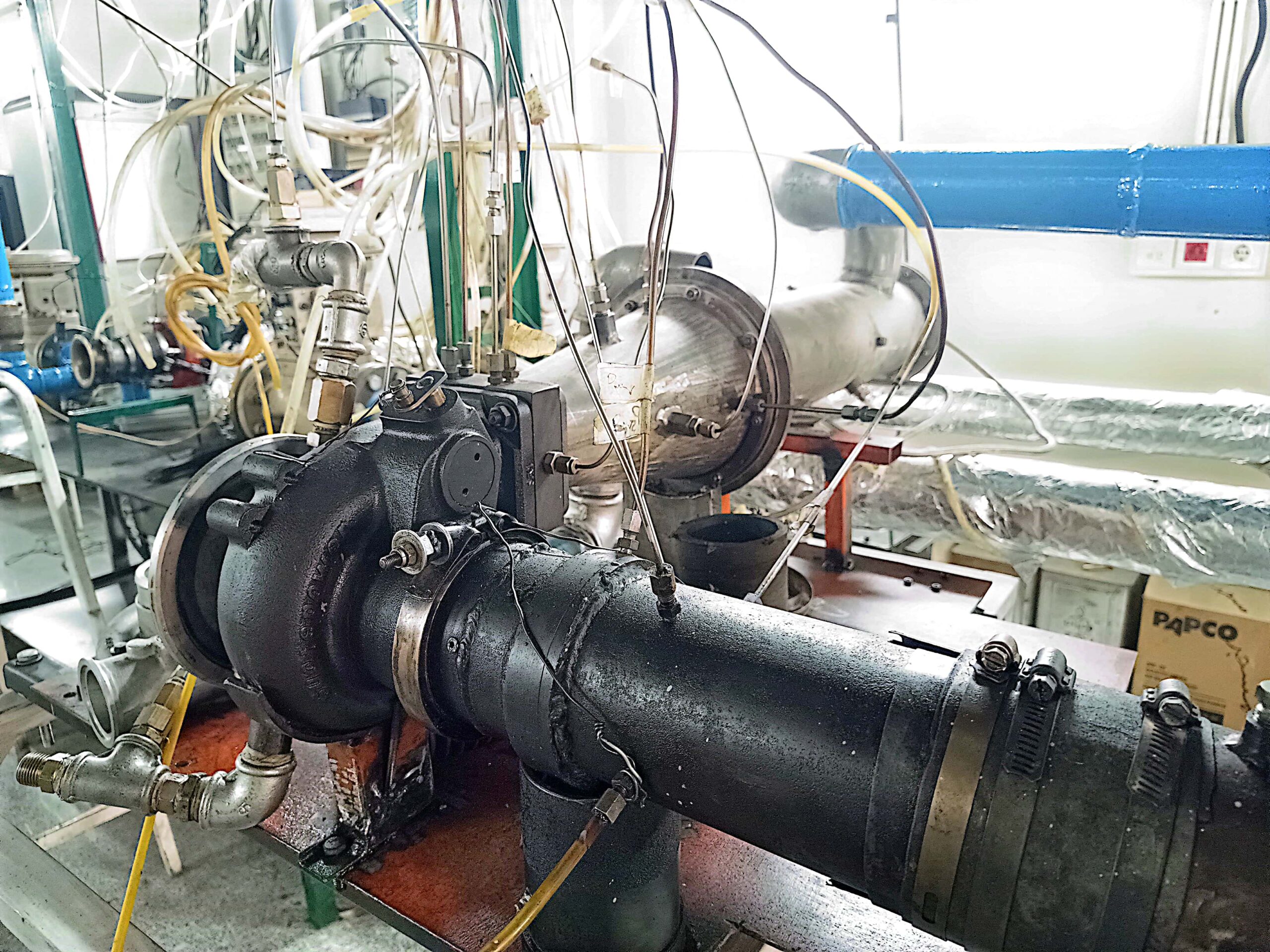

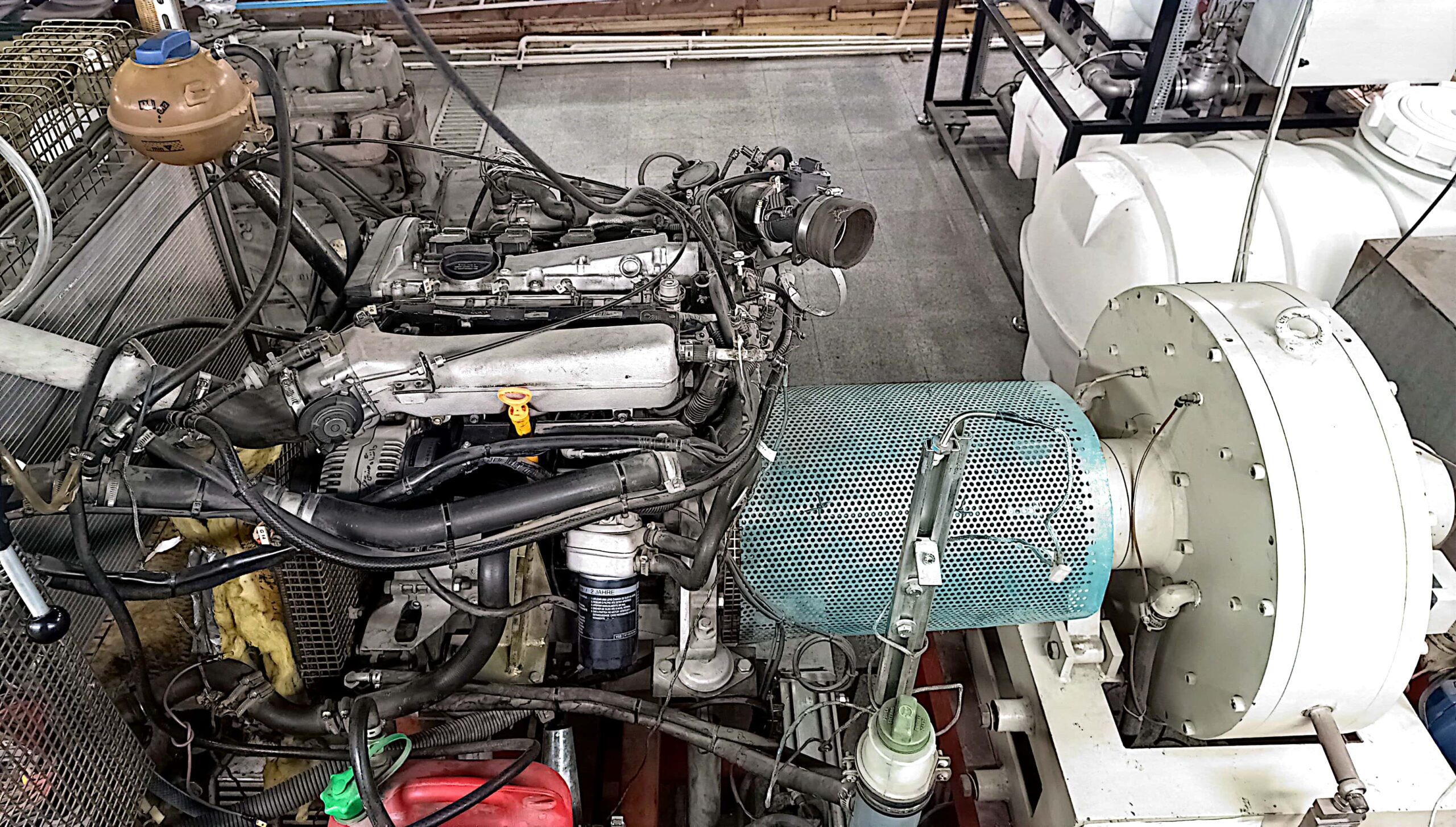
Turbocharging Test Bench
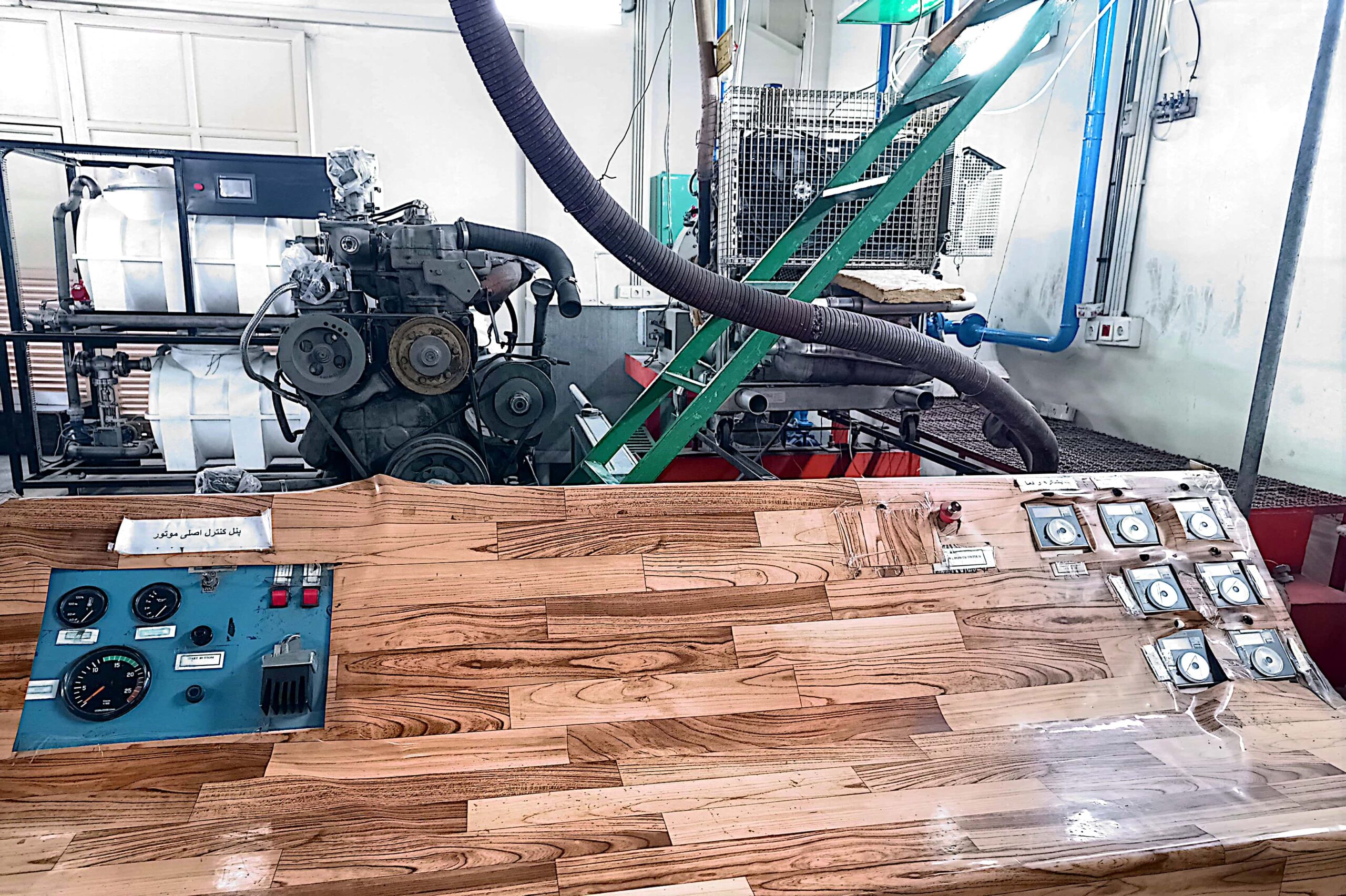



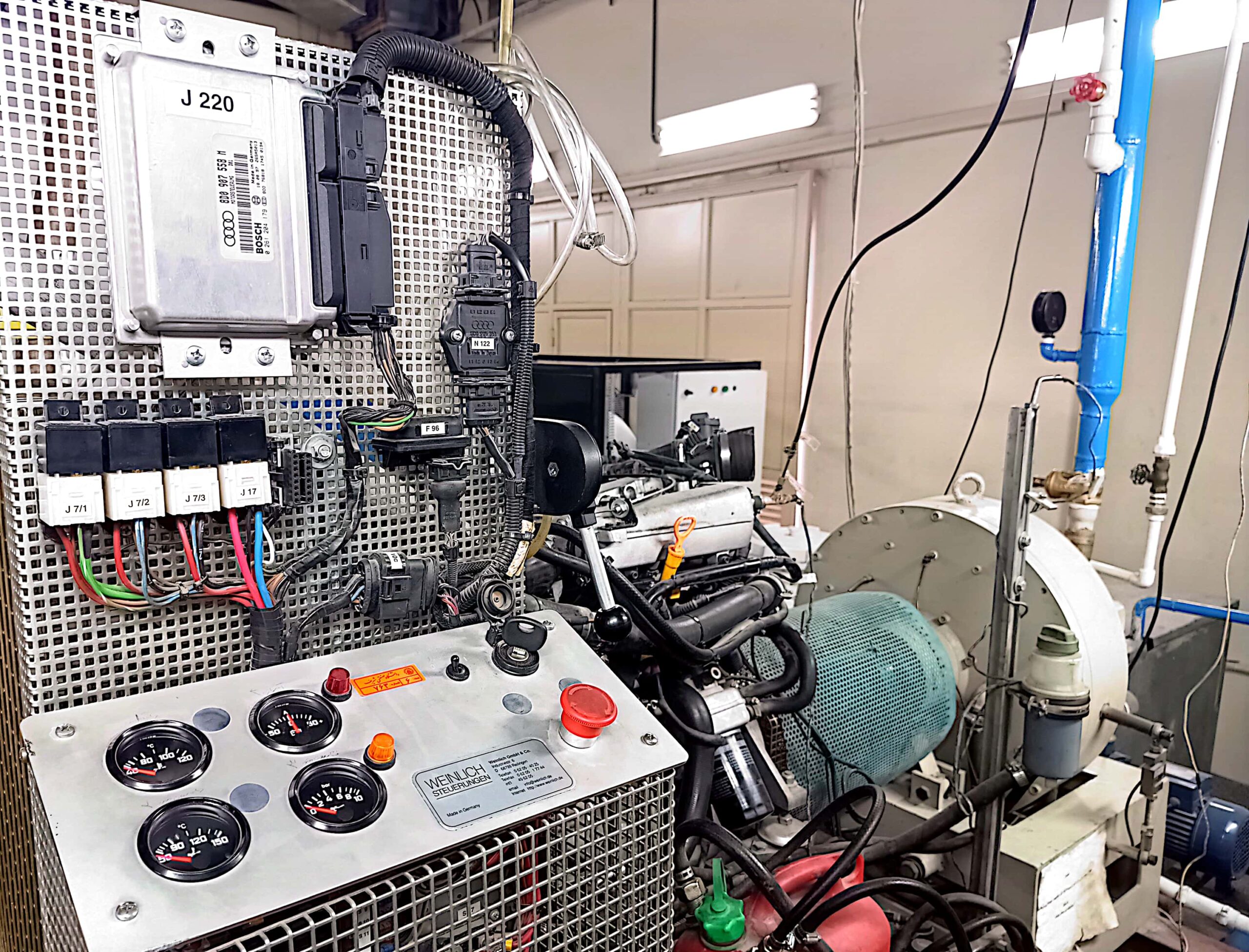
What is a Hot Turbocharger Test Rig?
✅A device that simulates real-world operating conditions of a turbocharger at very high temperatures (over 800°C) to evaluate its performance and durability.
What is the main purpose of a Cold Turbocharger Test Rig?
✅To test the turbocharger under non-combustion conditions, primarily for evaluating compressor performance, air leak detection, and airflow analysis under pressure.
What is the key difference between Hot and Cold testing?
✅ Hot testing simulates the high temperature of exhaust gases to test the turbine, while cold testing focuses on compressor and related system performance without combustion.
What is the primary industry application of these test rigs?
✅ Automotive industry (for passenger and commercial vehicles), marine, aerospace, and academic research.
What parameters are measured during Turbocharging testing?
✅Key parameters include pressure ratio, rotational speed (RPM), gas mass flow rate, inlet/outlet temperatures, and various efficiencies.
What is the main advantage of using a professionally designed test rig?
✅ Increased accuracy of results, repeatability of tests for validation, and long-term cost reduction through optimized design.
What is the role of the lubrication system in these test rigs?
✅ To reduce friction, cool rotating components (like bearings), and ensure the turbocharger’s durability under severe operating conditions.
What is "Surge Phenomenon" in a compressor and why is studying it important?
✅ Surge is a dangerous flow instability in compressors that can lead to damage. Identifying its contributing factors and prevention methods is a key testing objective.
What is a key capability common to all these test rigs?
✅ Conducting comprehensive theoretical and experimental studies on components, extracting performance characteristics, and modeling/optimizing the turbine and compressor.
How does a Turbocharging test rig help reduce emissions?
✅ By optimizing the turbocharger system and improving engine combustion efficiency, it leads to reduced fuel consumption and consequently lower pollutant emissions.



