Rotating equipment design
Practical experience
-
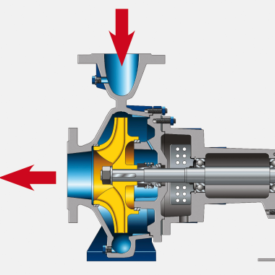
طراحی پمپ توربینی
Turbine Pump
-

طراحی هیدرولیکی پمپ 200 درجه سلسیوس
200-Degree Celsius Pump
-
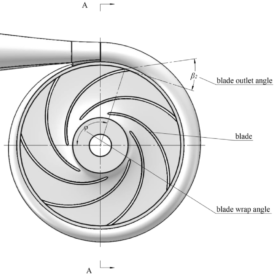
طراحی توربین جریان خروجی شعاعی
Radial Outflow Turbine
-
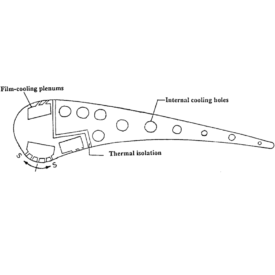
طراحی و بهینهسازی توربین C3X
C3X Turbine
Table of contents
Rotating Equipment Design | Principles, Concepts, and Specialized Engineering Services
Introduction
Rotating equipment are among the main components of production and process lines in heavy and semi-heavy industries. Any device that involves rotational motion—from pumps and compressors to turbines, fans, industrial blowers, and gearboxes—falls under rotating equipment. Designing this equipment is a multidisciplinary activity requiring a combination of mechanical engineering, dynamics, fluid mechanics, metallurgy, vibrations, and materials engineering.
Concept of Rotating Equipment Design
Rotating equipment design is a process of converting the functional requirements of a system into a reliable, efficient, and safe machine. In this design, engineers must consider characteristics such as rotational speed, required torque, energy efficiency, dynamic loads, environmental conditions, type of fluid, operating temperature, and pressure.
Proper design ensures that equipment:
Performs stably under real operating conditions,
Operates without excessive vibration,
Reduces energy consumption,
Increases the lifespan of equipment and components,
And significantly decreases maintenance costs and production downtime.
Importance of Proper Design in Industries
Rotating equipment design plays a vital role in every industry—especially oil, gas, petrochemical, water and wastewater, power generation, and mining.
Key reasons include:
1. Preventing Unexpected Failures
More than 40% of production downtime is related to rotating equipment. Proper design significantly reduces this risk.
2. Increasing Efficiency and Reducing Energy Consumption
A large portion of energy consumption in factories comes from pumps and fans. Correct selection of design parameters and materials directly impacts energy costs.
3. Compliance with Safety and Industrial Standards
Rotating equipment must be designed according to standards such as API, ISO, ASME, and ASTM to ensure safe and reliable performance.
4. Optimizing Life Cycle Cost (LCC)
Proper design is not limited to the manufacturing stage; it also optimizes repair costs, spare parts, energy consumption, and lifespan.
Stages of Rotating Equipment Design
1. Collection of Process Data
- Pressure and flow rate.
Fluid properties.
Temperature and environmental conditions.
Functional requirements and project constraints.
2. Conceptual Design
Determining the type of device (pump, compressor, fan, turbine, etc.).
Choosing the method of power transmission.
Preliminary estimation of efficiency and energy consumption.
3. Mechanical and Structural Design
Design of axle, bearing, shaft, and coupling.
Strength, fatigue, wear, and service life calculations.
Static and dynamic load analysis.
4. Vibration Analysis and Balancing
Modal analysis.
Investigation of natural frequencies.
Design of static and dynamic balancing system.
5. Fluid and Thermodynamic Analysis
Fluid flow simulation (CFD).
Thermal behavior and cooling analysis.
Prediction of cavitation in pumps.
6. Selection of Suitable Materials
Corrosion-resistant.
High temperature tolerance.
Suitable abrasion and fatigue resistance.
7. 3D Modeling and Simulation
Accurate computer-aided design (CAD) model.
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) to ensure the strength and performance of the device.
- CFD simulation for thermohydraulic analysis.
8. Preparation of Engineering Drawings and Documentation
Construction plans.
Bill of Materials
Analysis report and calculation notebook.
Sources for Rotating Equipment Design
Table of contents
Rotating equipment design




What is rotating equipment?
✅Rotating equipment includes any machinery with rotational motion such as pumps, compressors, turbines, fans, blowers, and gearboxes.
Why is the design of rotating equipment important?
✅Proper design increases reliability, reduces downtime, lowers energy consumption, and improves equipment lifespan.
What process data are required for designing rotating equipment?
✅Flow rate, pressure, fluid properties, temperature, environmental conditions, and operational requirements.
Why is vibration analysis essential?
✅To prevent resonance, reduce excessive vibrations, and ensure stable and safe operation.
What is the purpose of CFD in rotating equipment design?
✅To analyze fluid flow, predict cavitation, evaluate thermal behavior, and optimize hydraulic performance.
What materials are commonly used in rotating equipment?
✅Corrosion-resistant alloys, high-temperature steels, and wear-resistant materials depending on fluid type and conditions.
How does proper balancing improve equipment performance?
✅It reduces vibration, increases bearing life, and prevents fatigue and premature failure.
What standards apply to rotating equipment design?
✅API, ISO, ASME, and ASTM specifications depending on equipment type.
What documents are delivered at the end of the design process?
✅3D CAD models, FEA/CFD reports, BOM, fabrication drawings, and calculation booklets.
What factors affect the efficiency of rotating equipment?
✅Speed, torque, hydraulic design, mechanical losses, fluid characteristics, and operating conditions.



