Power Plant Design
Practical experience
-
Development of Technical Know-How for Steam Power Plant Design
-
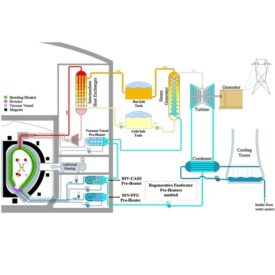
Conceptual and Basic Design of Steam Power Plant
-
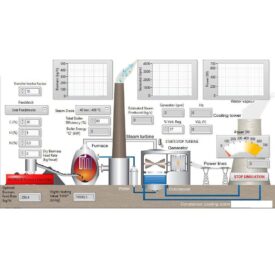
Steam Power Plant Simulator Design
-
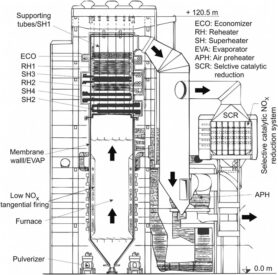
Steam Power Plant Detailed Design
Table of contents
Process Design Engineering
It is a branch of engineering that analyzes, designs, optimizes, and monitors industrial and manufacturing processes. This discipline plays a central role in converting raw materials into final products and aims to create economical, safe, efficient, and sustainable processes. This field is highly significant in various industries, including oil and gas, petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, food production, and energy.
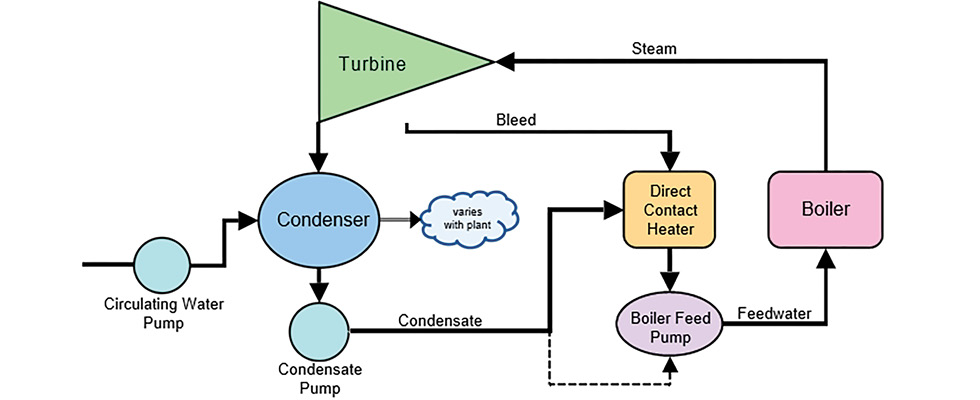
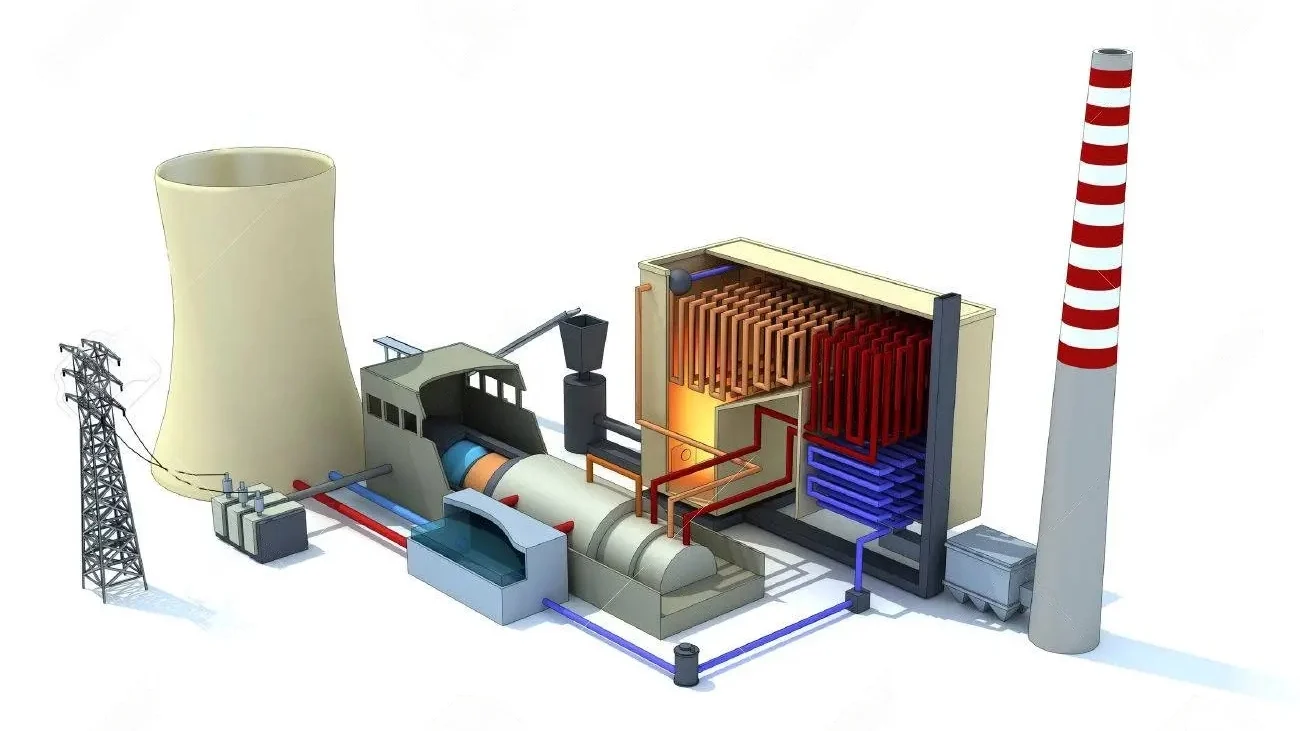
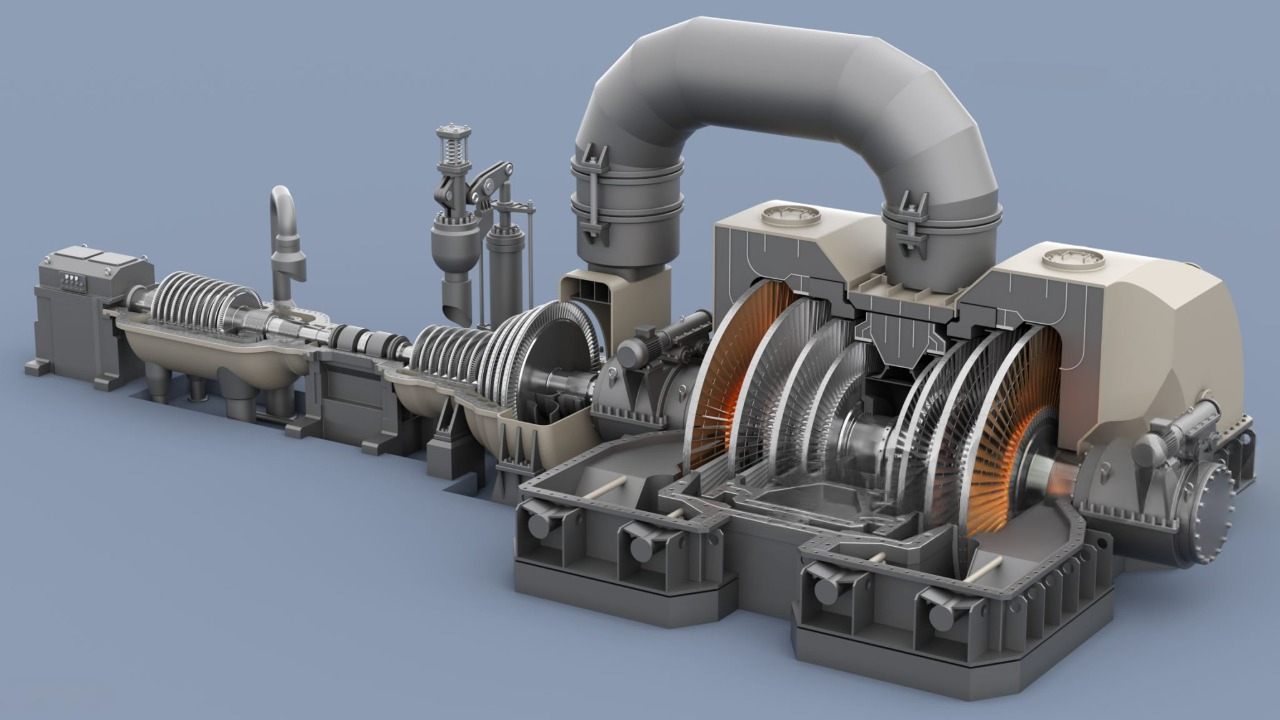
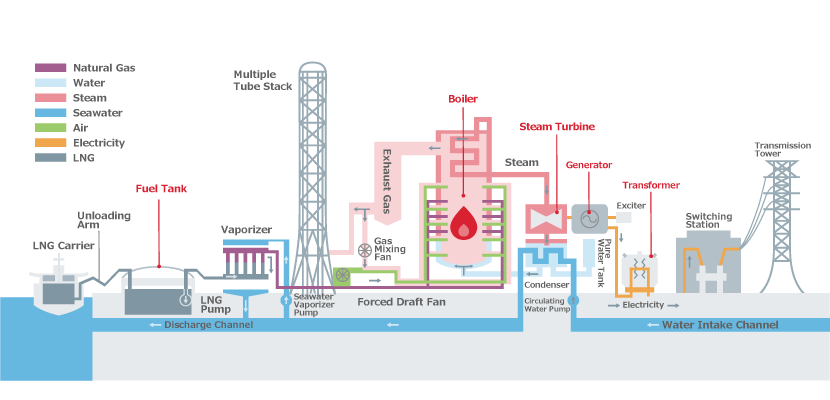
In steam power plants, process design engineering plays a key role in converting thermal energy into electrical energy. Process design in these systems involves the selection and arrangement of main components such as boilers, turbines, condensers, pumps, and heat exchangers to optimize energy and fluid flow. In this regard, the process engineer must consider factors such as thermal efficiency, operational safety, energy loss reduction, reliability, and environmental compliance. Detailed analysis of energy balance, design of steam and feedwater circuits, and determination of optimal equipment operating conditions are among the most important tasks in the process design of a steam power plant.
Research and Development in Thermal Power Plant Process Design
Research and Development (R&D) plays a fundamental role in the design and optimization of thermal power plants. Particularly when the goal is to achieve an optimal design or improve system efficiency, there is a need for thorough testing and evaluation of various options. Research projects in this field typically progress using Technology Readiness Level (TRL) models, where each technology and design is assessed at different stages. From selecting suitable materials to withstand high pressures and temperatures in boilers to developing more efficient gas and steam turbines, each stage is meticulously examined with the aim of enhancing performance and reducing costs.
In power plant research and development projects, process engineering teams meticulously analyze various design options. These options may include the selection of turbine types, boiler design, evaluation of heat recovery systems, or the choice of different fuels. Each selection can significantly impact the plant’s efficiency, cost, and overall performance. For instance, in the design of combined cycle power plants, both gas and steam turbines are utilized simultaneously to optimally harness both energy sources.
Achieving an optimal process design for the desired objective.
Ultimately, achieving an optimal design is the goal of process design and engineering in thermal power plants, which helps produce energy with the highest efficiency and minimal loss. These designs can pursue various objectives: increasing energy efficiency, flexibility in power generation, and reducing costs. In a thermal power plant, efficiency means converting the maximum amount of thermal energy into power. The higher the system efficiency, the less fuel is needed to generate power, resulting in lower operational costs. Additionally, flexibility in process design allows power plants to meet the changing and diverse needs of different industries. For example, sometimes the demand for power may suddenly increase, and at such times the system must be able to quickly adjust the power output. In thermal power plant design, especially in advanced designs and research projects, attention to these issues is crucial.
By implementing research and development at every design stage, process engineering teams can select the optimal configuration and design for each specific project. These designs not only enhance efficiency and reduce costs but also contribute to achieving specific project objectives such as increased flexibility and reduced environmental impact. In R&D projects, various design and process options are meticulously evaluated using simulation and modeling techniques to identify the best solutions for specific project conditions.
Objectives of Process Design Engineering
- Optimization of Production:
Designing processes with maximum productivity and minimum cost. - Enhancing Safety:
Ensuring processes are executed to minimize human and environmental risks. - Environmental Sustainability:
Designing processes with minimal negative environmental impact. - Compliance with Standards:
Adherence of processes to international standards such as API, ASME, and ISO.
Key Stages of Process Design Engineering:
- Preliminary Study and Data Collection:
Review of raw material specifications, products, and operational conditions. This stage involves studying the physical and chemical properties of materials and assessing market requirements. - Developing Process Flow Diagrams (PFDs).
- Process Flow Diagram (PFD): Includes general process information such as material flows, temperature and pressure conditions, and major equipment.
- Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID): Detailed representation of pipes, valves, sensors, and other instrumentation equipment.
- Modeling and Simulation:
Utilizing engineering software such as Aspen HYSYS, CHEMCAD, and ANSYS to predict process performance and evaluate various alternatives. - Equipment Selection:
Determining required equipment such as heat exchangers, reactors, distillation columns, pumps, and compressors based on operational conditions. - Design Calculations:
Performing precise thermodynamic, heat transfer, and mass transfer calculations for optimal equipment and production line design. - Economic Analysis and Evaluation:
Reviewing capital, operational, and maintenance costs to determine the most economical solution. - Safety and Environmental Assessment:
Identifying and managing process risks and ensuring compliance with environmental requirements.
Tools and Software Used
- Aspen Plus / HYSYS: Process simulation.
- CHEMCAD: Flow and equipment modeling.
- MATLAB: Process analysis and optimization.
- AutoCAD / PDMS: 3D equipment and piping design.
- ANSYS / FLUENT: Computational fluid dynamics and heat transfer analysis.
Applications of Process Design Engineering:
- Oil, Gas & Petrochemical Industries:
Design of refining units, polymer production units, and industrial gas facilities. - Pharmaceutical Industry:
Drug manufacturing under specific safety and hygiene conditions. - Food Industry:
Design of food production, packaging, and preservation processes. - Power Generation Industries:
Design of thermal power plants, combined cycle systems, and renewable energy facilities. - Water and Wastewater Industries:
Design of water treatment systems and effluent recycling.
Key Skills in Process Design Engineering
- In-depth knowledge of engineering principles
- Thermodynamics
- Heat Transfer
- Mass Transfer
- Ability to analyze and model:
Process simulation for performance improvement. - Proficiency in engineering standards:
Such as ASME, API, and ASTM. - Communication and teamwork skills:
For collaboration with interdisciplinary teams. - Problem-solving and decision-making:
Finding optimal solutions for industrial challenges.
Challenges & Opportunities
- Challenges:
- Changes in energy and raw material prices.
- Pollutant management.
- The need for innovation to compete in the market.
- Opportunities:
- Development of green technologies.
- Increasing demand for renewable energy.
- The use of artificial intelligence in process simulation and optimization.
Advanced power plant dynamic analysis services
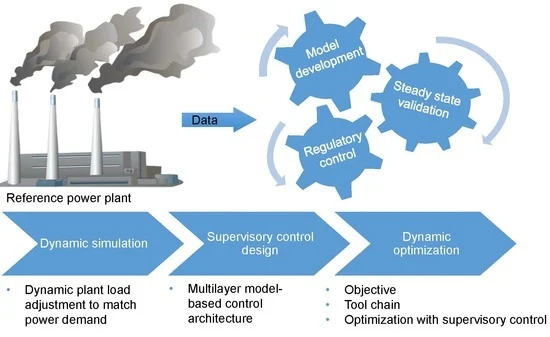
Our center, with a focus on development and continuous improvement, provides advanced services in the field of power plant system dynamic analysis. Utilizing modern simulation methods and engineering tools, we strive to provide effective solutions for the analysis, control, and optimization of power plants. Our workflow consists of three main stages: dynamic simulation, supervisory control system design, and dynamic optimization.
In the initial step, operational data from reference power plants are utilized to simulate the system’s dynamic behavior. This phase aids in better understanding the system’s performance under various operational conditions. Subsequently, the supervisory control system design is implemented using a multi-layer model architecture approach, aiming to enhance system accuracy and reliability. In the final step, dynamic optimization is employed to investigate various methods for improving performance and reducing the system’s response time to changes.
While the development path of this technology continues, our commitment to learning and innovation guarantees the delivery of services aligned with current global standards. Collaborating with our center enables you to benefit from dynamic and up-to-date solutions for optimizing your power plant systems.
Process Design References
Table of contents
Power Plant Design
What is the Process Design Engineering?
✅ It is a branch of engineering that deals with the analysis, design, optimization, and supervision of industrial and production processes in order to create processes that are safe, economical, and sustainable.
What industries is process design engineering used in?
✅ It is a branch of engineering that deals with the analysis, design, optimization, and supervision of industrial and production processes in order to create processes that are safe, economical, and sustainable.
What are the duties of a process design engineer in a steam power plant?
✅ Selection and arrangement of main components such as the steam boiler, turbine, condenser, and pumps; optimization of energy and fluid flows; and evaluation of efficiency, safety, and environmental compatibility.
What is the role of Research and Development (R&D) in the design of thermal power plants?
✅ Evaluation of various design options with the aim of increasing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving equipment performance through precise modeling and simulation.
What do process diagrams include?
✅ Process Flow Diagrams (PFD) and Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&ID) that show material flows, temperature, pressure, and equipment layout.
What software is used in process design?
✅ Aspen HYSYS, CHEMCAD, MATLAB, AutoCAD, PDMS, ANSYS, and FLUENT are used for process simulation and analysis.
What are the main objectives of process design engineering?
✅ Optimization of production, increased safety, environmental sustainability, and compliance with international standards such as API, ASME, and ISO.
What skills does process design engineering require?
✅ Knowledge of engineering principles (thermodynamics, heat and mass transfer), process simulation, mastery of standards, communication skills, and problem-solving ability.
What are the main challenges in process design engineering?
✅ Fluctuations in energy prices, pollutant management, and the need for innovation to remain competitive in the market.
What stages are included in advanced power plant dynamic analysis services?
✅ Dynamic simulation, design of supervisory control systems, and dynamic optimization to increase accuracy and improve power plant performance.



