Thermohydraulic analysis of equipment
Practical experience
-
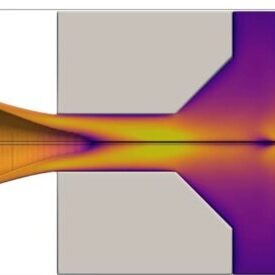
مطالعه پارامتری جریان درون نازل
Flow in a nozzle
-
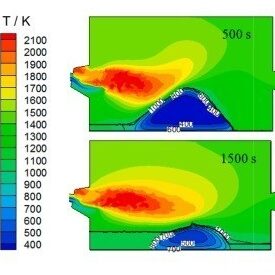
تحلیل نرخ ذوب کوره آلومینیوم
Aluminum Melting Furnace
-
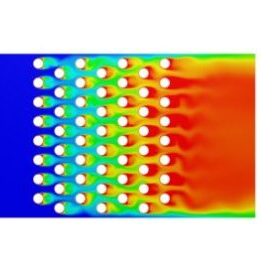
تحلیل افت فشار جریان عبوری از بانک لولهها
Flow Through Tube Banks
-
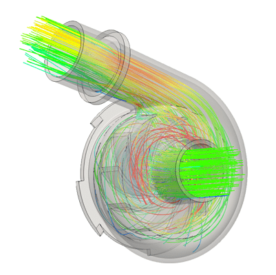
تحلیل توربین جریان شعاعی
Centrifugal turbine
-
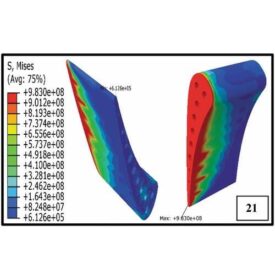
تحلیل توربین C3X
C3X Turbine
Table of contents
Thermohydraulic analysis of equipment
Introduction
Thermohydraulic analysis is an integrated engineering approach that combines knowledge of thermodynamics and fluid mechanics to accurately evaluate the performance, safety, and efficiency of equipment involved in heat transfer and fluid flow.
Main object
Ensuring equipment operates within safe temperature and pressure ranges while meeting design requirements (e.g. heat transfer rate, efficiency, temperature distribution).
چرا تحلیل ترموهیدرولیکی تجهیزات حیاتی است؟
In many industrial systems, thermal and hydraulic phenomena are inextricably intertwined:
Changing temperature changes the properties of the fluid (such as density and viscosity) and therefore the flow pattern.
The flow pattern directly affects the rate of heat transfer.
This interaction can lead to complex phenomena such as natural circulation (fluid movement based on density differences) or two-phase flow (boiling and condensation).
Key areas of analysis
1. Thermal analysis
Predicting temperature distribution and identifying hot spots in components.
Calculation of heat transfer rate.
Evaluation of thermal stresses caused by non-uniform expansion.
Review of the system’s thermal efficiency.
2. Hydraulic analysis
Calculating pressure drop throughout the system and ensuring proper pump operation.
Identification of flow regime (turbulent or laminar).
Examining flow stability and preventing destructive phenomena such as cavitation.
Uniform flow distribution in heat exchangers.
Equipment covered by this analysis
Heat exchangers (shell and tube, plate, finned).
The cores of reactors and their cooling systems.
Boilers, condensers, and steam generators.
Engine cooling systems, radiators, and electronic coolers.
Industrial piping networks and hydraulic loops.
Chemical reactors with exothermic or endothermic reactions.
Advanced analytical methods in the engineering center
At our engineering center, we perform these complex assessments using the latest software and analytical methods.
One-dimensional modeling
To analyze the behavior of the entire system under expected operating conditions and accidents, we use (1D) system codes such as RELAP5 and ATHLET. This method is ideal for simulating the overall performance of the power plant or cooling loops.
CFD modeling
For accurate, three-dimensional simulation of flow, temperature, and stress fields in complex geometries, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is used with software such as ANSYS Fluent. This method is very powerful for optimizing the design of specific components.
Our work process at the engineering center
The work process begins with defining the project objective and scope. Then, boundary conditions are determined and a suitable model is built. After running the simulation, critical results such as maximum temperature and pressure drop are analyzed and compared to design standards. Finally, a comprehensive report is provided with optimization suggestions.
Industrial applications
The applications of this analysis are wide-ranging. It is used in the power plant industry for the design and safety assessment of cooling systems, in the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries for the design of converters and reactors, in the aerospace field for the thermal management of advanced systems, in the automotive industry for the design of cooling systems, and in the electronics industry for the cooling of high-power components.
Thermohydraulic analysis of equipment references
Table of contents
Thermohydraulic analysis of equipment
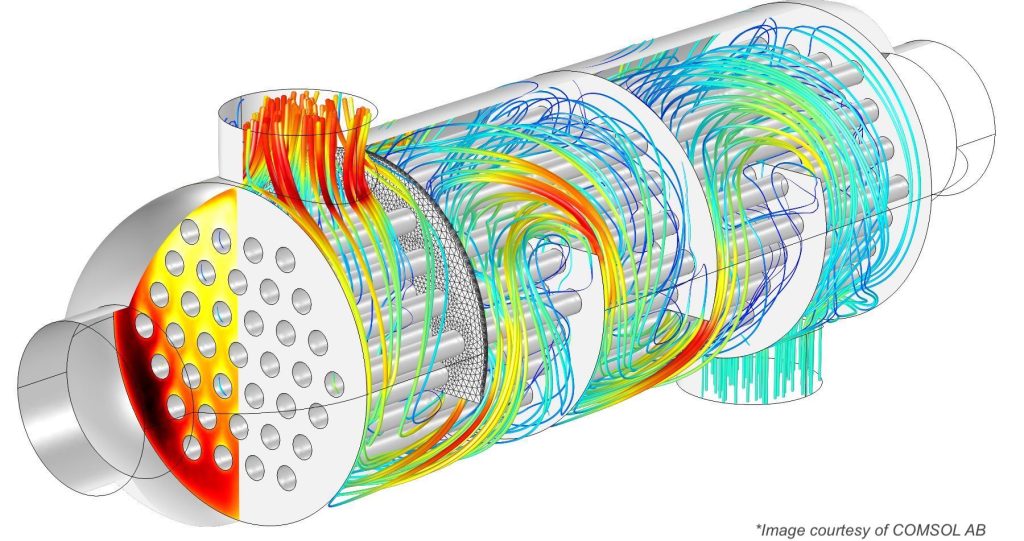
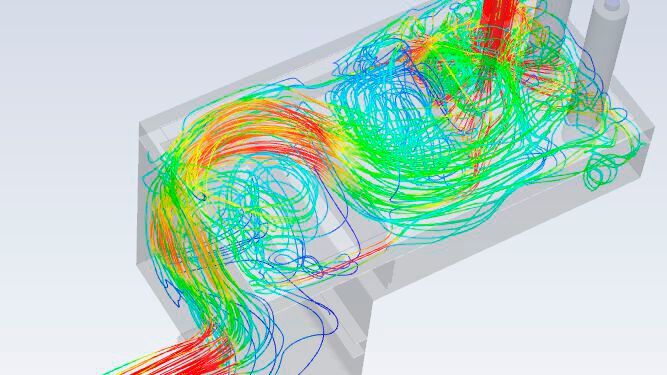

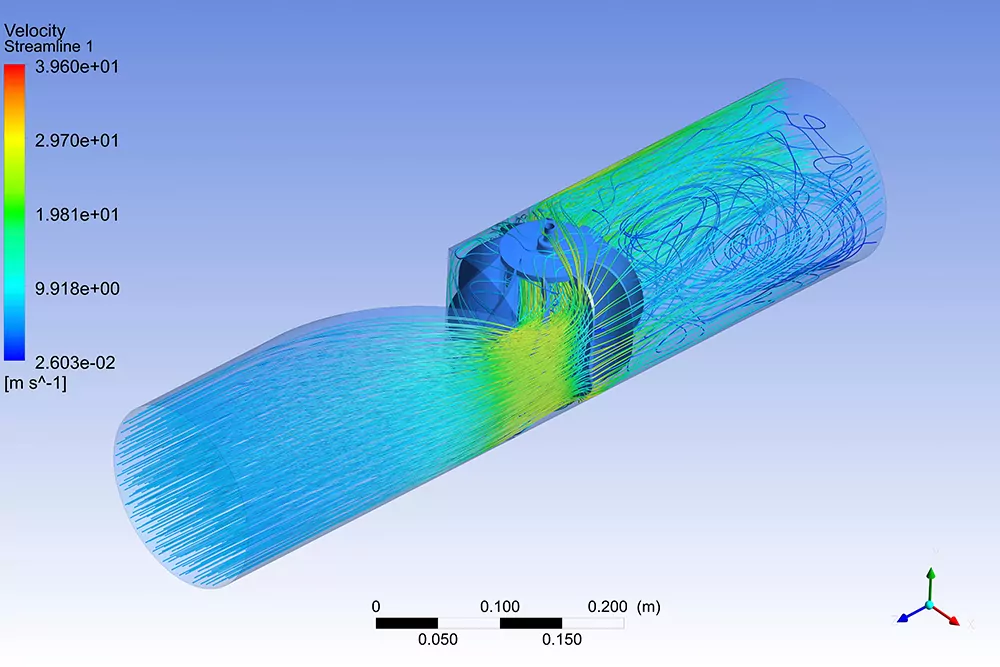
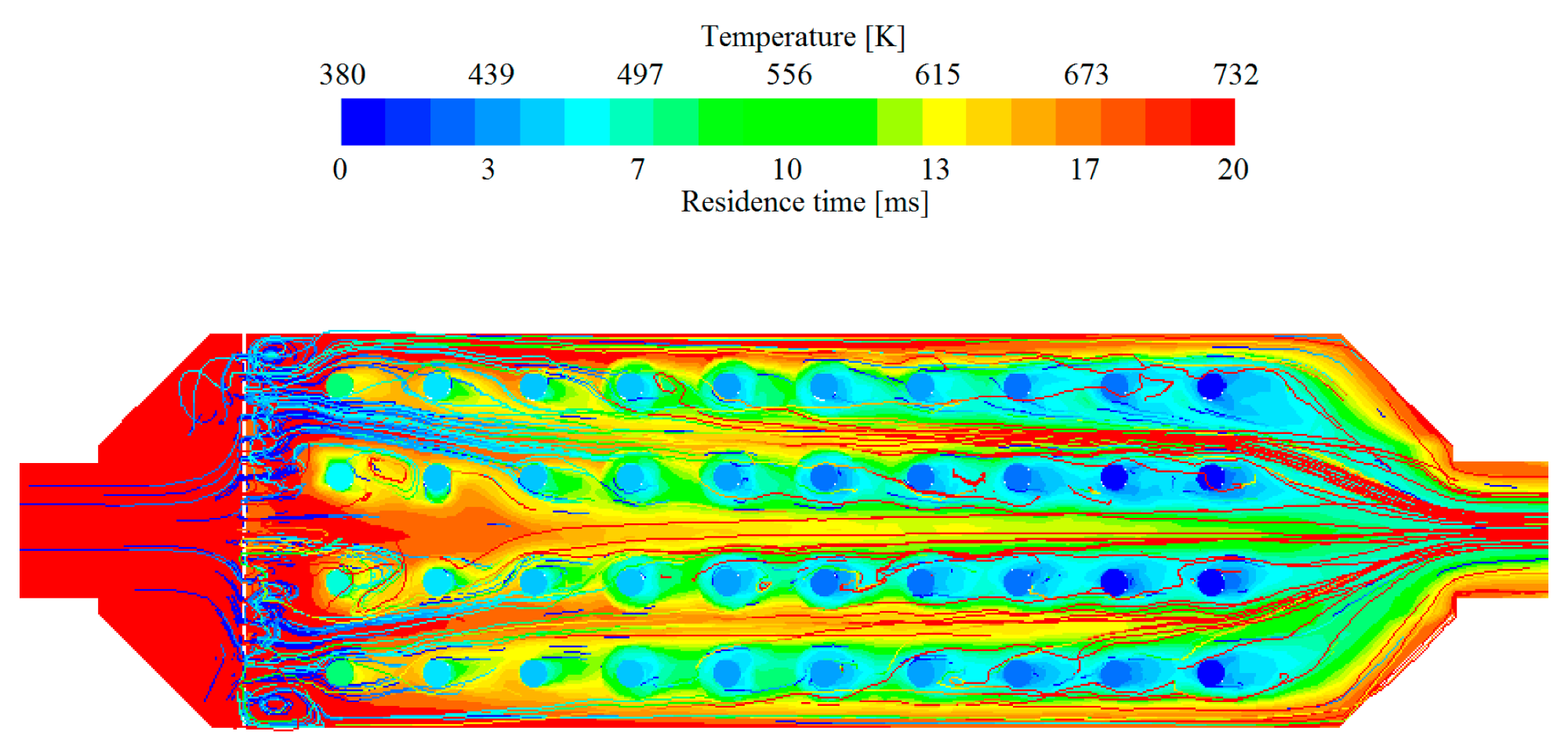
What is thermohydraulic analysis?
✅It is a combination of thermal and hydraulic analysis to simultaneously investigate heat transfer and fluid flow behavior in a system.
What is the main purpose of this analysis?
✅The main goal is to ensure the safe and efficient operation of equipment under design conditions and prevent failure due to thermal or hydraulic factors.
What equipment is this analysis necessary for?
✅For any equipment where there is fluid flow and heat exchange, such as heat exchangers, boilers, cooling systems, reactors and complex piping networks.
What are the most important outputs of this analysis?
✅The most important outputs include the temperature and pressure distribution in the system, heat transfer rate, total pressure drop, identification of critical points (such as hot spots or cavitation), and safety margins up to limit conditions.
What is the difference between thermohydraulic analysis and conventional CFD analysis?
✅Thermohydraulic analysis often models the entire system (System-Level), while CFD typically focuses on the flow details at a specific component (Component-Level). The two methods can be complementary.
What is the phenomenon of natural circulation?
✅Spontaneous movement of fluid due to density differences caused by temperature gradients, without the need for a pump. This phenomenon is very important for passive safety systems in sensitive industries.
How does thermohydraulic analysis help optimize energy consumption?
✅By identifying unnecessary heat losses, areas with high pressure drop, and inefficient heat transfer, it provides solutions to reduce pump energy consumption and improve thermal efficiency.
Is this analysis only for designing new equipment?
✅No. This analysis is also very useful for troubleshooting performance problems in existing systems, assessing safety after changes are made, and optimizing the performance of operating equipment.
What factors does the accuracy of these analyses depend on?
✅Accuracy depends on the quality of the input data (fluid properties, boundary conditions), validated mathematical models for complex phenomena (such as boiling), and validation of the results with laboratory or operational data.
Why should we entrust this analysis to your engineering center?
✅With deep experience in various industrial projects, we offer access to up-to-date specialized software and a systematic approach, accurate, practical and reliable analysis to make the best technical and economic decisions.



