Uncertainty and Reliability Analysis
As a leading center in advanced uncertainty and reliability analysis, we deliver transformative industrial solutions by combining deep engineering expertise with cutting-edge artificial intelligence technologies.
Table of contents
Uncertainty and Reliability Analysis
Uncertainty
Every piece of equipment faces some probability of deviation from the parameters that affect its performance—this is known as uncertainty. In practice, due to measurement limitations, environmental variations, process fluctuations, or modeling imperfections, the actual values of these parameters may differ from predicted or design values. In other words, uncertainty represents the degree of unknowns or variability that can influence real-world outcomes and make accurate performance prediction challenging. More formally, uncertainty is defined as the potential for error in system behavior or its prediction arising from incomplete information or knowledge.
Reliability
Reliability is the probability that a system or component will successfully perform its required function under stated conditions for a specified period of time. It reflects the level of confidence in the correctness and stability of equipment performance throughout its operational life. Highly reliable equipment maintains its expected performance with high probability even when subjected to real-world environmental factors, workloads, and operating conditions.
Advanced Uncertainty Analysis Methods
1. Numerical and Statistical Methods
Monte Carlo Simulation: Running thousands of scenarios using different probability distributions
Global Sensitivity Analysis: Identifying the most influential parameters driving uncertainty
Non-linear Regression Models: Capturing complex relationships between variables
2. Artificial Intelligence-Based Methods
Bayesian Neural Networks: Modeling uncertainty in predictions
Probabilistic Support Vector Machines: Sensitivity analysis using machine learning
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for noisy data: Extracting patterns from scattered/uncertain datasets
Modern Reliability Assessment Techniques
1. Advanced Analytical Methods
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA): Identifying critical failure combinations
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): Systematic risk evaluation
Markov Modeling: Analyzing systems with multiple performance states
2. Data-Driven Approaches
Deep Learning-Based Survival Models: Predicting time-to-failure distributions
Anomaly Detection Systems: Early identification of abnormal behavior before failure
Equipment Life Data Analysis: Learning from historical performance records
Integration of Uncertainty and Reliability
Integrated Frameworks
RBDO (Reliability-Based Design Optimization): Design optimization that explicitly accounts for reliability constraints
RBR (Reliability-Based Robustness) Analysis: Assessing resilience under uncertain conditions
Physics-Informed Machine Learning Models: Combining governing equations with operational data
Advanced Industrial Applications
In Process Design
Optimization Under Uncertainty: Creating processes that remain stable despite variable conditions
Quantitative Risk Analysis: Calculating probabilities of critical scenarios (<= Probability of Failure, Risk Priority Numbers)
In Asset Management
Risk-Based Maintenance Planning: Allocating resources according to reliability predictions
Spare Parts Inventory Optimization: Determining optimal stock levels considering uncertainty
Industrial Implementation Steps
Implementation Steps
Identify Uncertainty Sources: Complete listing of uncertain parameters
Quantify Uncertainties: Assign appropriate statistical distributions
Model Reliability: Develop limit-state functions
Integrated Analysis: Execute combined probabilistic simulations
System Optimization: Find robust and reliable designs
Recommended Software Tools
ANSYS Workbench: Uncertainty & probabilistic design
ReliaSoft suite: Comprehensive reliability engineering
Python libraries: PyMC3, TensorFlow Probability, chaospy, UQpy
Summary and Value Creation
Modern uncertainty and reliability analysis enables:
Data-Driven Decision Making instead of pure experience
Robust Designs resilient to real-world variations
Proactive Risk Management before failures occur
Continuous Improvement through machine learning
Uncertainty and Reliability Analysis References
Table of contents
Uncertainty and Reliability Analysis
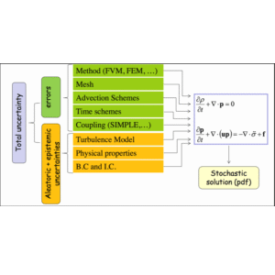
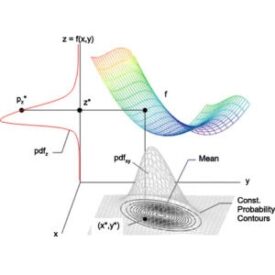
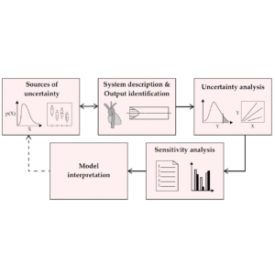
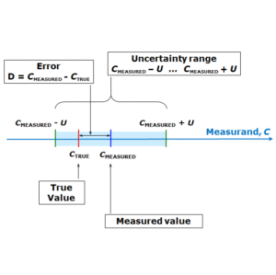
What does uncertainty mean in industrial systems?
✅ The difference between actual and predicted values of parameters affecting performance, arising from measurement limits, environmental fluctuations, modeling gaps, or incomplete knowledge.
What is reliability and why is it important?
✅ The probability of successful operation under defined conditions for a given time; it is a key indicator of system stability and confidence in real-world deployment.
Which numerical methods are used for uncertainty analysis?
✅ Monte Carlo simulation, global sensitivity analysis, and non-linear regression models.
How can AI help analyze uncertainty?
✅ Bayesian neural networks, probabilistic SVMs, and CNNs extract hidden patterns and quantify uncertainty even from noisy or incomplete datasets.
What are the modern methods for reliability assessment?
✅ Fault Tree Analysis (FTA), FMEA, Markov models, deep-learning survival analysis, and anomaly detection systems.
What role does machine learning play in reliability prediction?
✅ Deep survival models, anomaly detection, and historical life-data analysis provide far more accurate failure forecasts than traditional statistical methods.
What is RBDO and its benefit?
✅ Reliability-Based Design Optimization produces designs that are both highly efficient and reliably meet performance requirements under uncertainty.
How are uncertainty and reliability analyses integrated?
✅ Through physics-informed ML, RBR analysis, and robust optimization frameworks that evaluate both risk and resilience simultaneously.
In which industrial areas are these analyses applied?
✅ Robust process design, quantitative risk assessment, risk-based maintenance, and spare-parts inventory optimization.
Which tools are recommended for advanced analyses?
✅ ANSYS Workbench (uncertainty), ReliaSoft (reliability), and Python libraries PyMC3 & TensorFlow Probability.



