Design and Optimization of Turbomachines
At our research center, we deliver innovative solutions for the design and optimization of turbomachines by combining the latest advances in mechanical engineering, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), and Artificial Intelligence.
Table of contents
Design and Optimization of Turbomachines
Definition and Classification of Turbomachinery
Turbomachines are rotating machines that transfer energy between a fluid and a rotor through changes in angular momentum. They are divided into two main groups:
1.Power-Delivering Turbomachinery (Turbines)
- Gas Turbines.
- Steam Turbines.
- Hydraulic Turbines.
2. Power-Absorbing Turbomachinery (Compressors and Pumps)
- Axial Compressors.
- Centrifugal Compressors.
- Centrifugal Pumps.
Common Features
- Presence of a rotating rotor with aerodynamic blades.
- Continuous and uninterrupted energy transfer.
- Dependence of performance on working fluid properties.
Importance of Turbomachinery in Industry
1. Role in Energy Infrastructure
- Production of over 60% of the world’s electricity by steam and gas turbines.
- Consumption of 40% of industrial energy in pumping and compressor systems.
2. Strategic Applications
- Oil and Gas Industry: From extraction to refining.
- Thermal and Nuclear Power Plants.
- Industrial ventilation and refrigeration systems.
- Aerospace industry and jet engines.
3. Major Industrial Challenges
- A 1% increase in gas turbine efficiency = million-dollar savings.
- Reducing energy consumption of pumping systems in chemical industries.
- Need for equipment with longer operational life in harsh conditions.
Governing Thermodynamic Principles
1. Fundamental Equations
- Euler energy equation for turbomachinery.
- Relationship between velocity triangles and energy transfer.
- Concept of reaction degree and its impact on design.
2. Key Performance Parameters
- Overall Pressure Ratio.
- Isentropic Efficiency.
- Specific Speed.
3. Thermodynamic Limitations
- Effects of compressibility in high-speed flows.
- Cavitation phenomenon in pumps.
- Limitations arising from the second law of thermodynamics.
Energy Transfer Mechanisms
1. In Turbines
- Conversion of thermal energy to mechanical energy.
- Effect of blade angles on energy extraction.
- Stage loading phenomenon.
2. In Compressors and Pumps
- Pressure increase mechanism in axial and radial flows.
- Role of centrifugal force in centrifugal compressors.
- Importance of diffuser design in energy efficiency.
3. Complex Flow Phenomena
- Boundary layer separation at high angles of attack.
- Formation of blade tip vortices.
- Stage interaction effects.
Historical Developments and Modern Advances
1. Design Evolution
- From simple 19th-century hydraulic turbines to modern systems.
- Revolution in materials and manufacturing methods.
- Transformation in analysis and simulation methods.
2. Modern Technologies
- Use of advanced composites in blades.
- Modern cooling systems.
- Integration of intelligent sensors.
3. Future Research
- Development of adaptive turbomachinery.
- Applications of artificial intelligence in performance control.
- Sustainable development approaches in design.
Summary and Importance of Center's Research
Given the technical complexity and strategic importance of turbomachines, our center’s research is focused on three pillars:
Developing more accurate analytical methods.
Optimizing existing systems with digital technologies.
Providing practical solutions for industry.
This deep expertise forms the foundation for our specialized turbomachinery design and optimization services.
Turbomachinery design and optimization references
Table of contents
Turbomachinery design and optimization
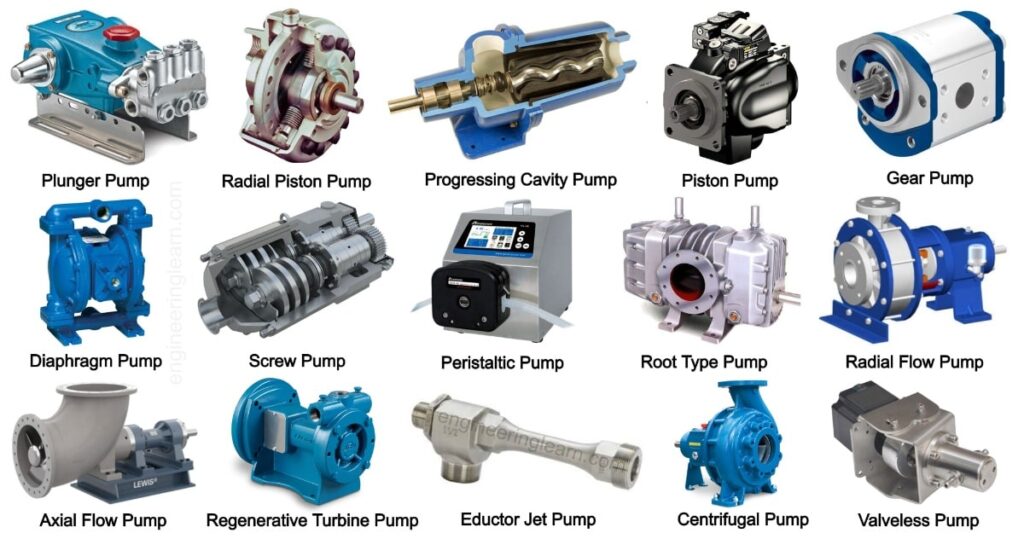
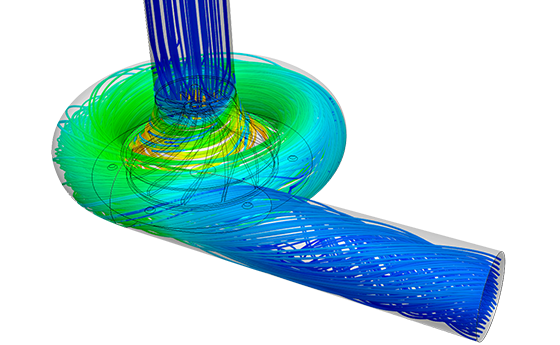
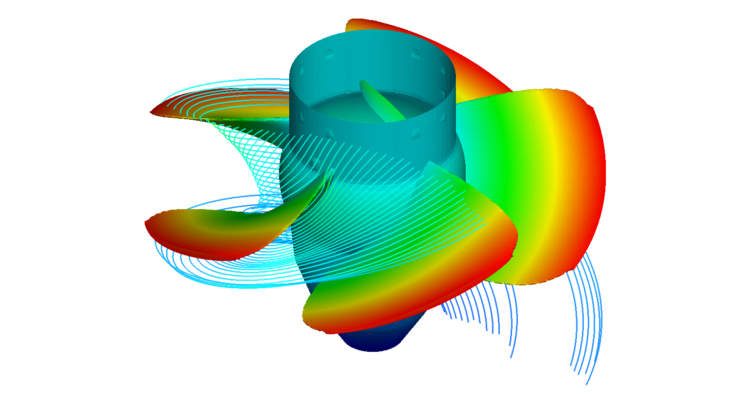
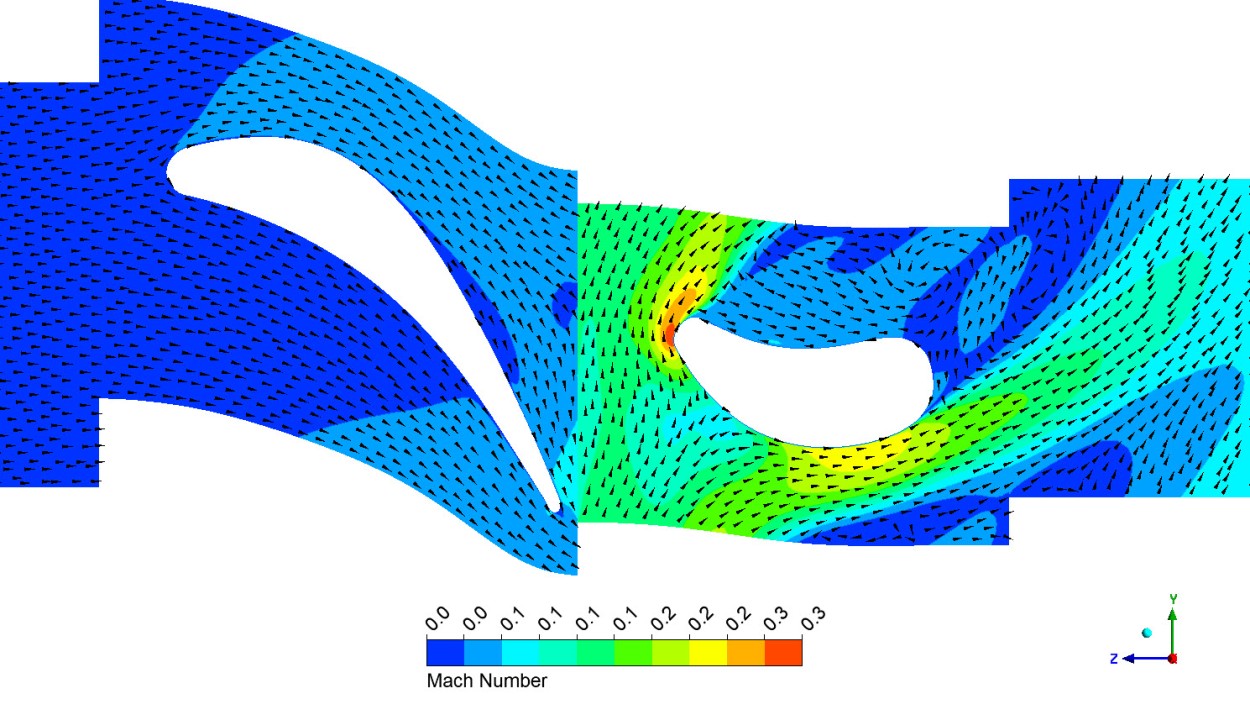


What is a turbomachine?
✅ A turbomachine is a rotating device that transfers energy between a fluid and the machine (or vice versa) using a rotor and aerodynamic blades through a change in angular momentum.
How are turbomachines classified?
They are divided into two main categories:
✅ Power-generating turbomachines (such as gas, steam, and hydro turbines)
✅ Power-absorbing turbomachines (such as compressors and pumps)
What are the main industrial applications?
✅ Power generation, oil & gas, jet engines, large-scale HVAC, refrigeration, and almost every energy-intensive process.
Why is even a 1% efficiency gain economically significant?
✅ It translates into millions of dollars in fuel savings and reduced CO₂ emissions over the machine’s lifetime.
What are the key thermodynamic principles?
✅ Euler equation, velocity triangles, degree of reaction, pressure ratio, isentropic efficiency, specific speed.
What are the primary thermodynamic challenges?
✅ Flow compressibility, cavitation in pumps, and second-law irreversibilities.
How is energy transferred in turbines vs. compressors/pumps?
✅ Turbines extract work from the fluid (expansion); compressors/pumps add work to the fluid (compression) using axial or centrifugal mechanisms.
What are the latest advances in turbomachinery?
✅ Fluid pressure is increased using axial flow mechanisms, centrifugal force, and proper diffuser design.
What are the latest advances in turbomachinery?
✅ Advanced composites, sophisticated cooling techniques, additive manufacturing, AI-driven control, and adaptive geometries.
What are the main research axes of your center?
✅ Advanced analytical/numerical methods, digital optimization of legacy systems, and industry-ready design & diagnostic solutions.



